Adversarial Search & Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Soal :
1. Apa yang dimaksud Adversarial Search & Constraint Satisfaction Problems ? berikan contoh ?
2. Apa itu Propositional Logic ? berikan contoh ?
3. Buat coding (Boleh C, C++ atau Java) untuk Algoritma A & Algoritma A* (A Star )?
1. – Adversarial Search :
Algoritma pencarian yang memeriksa masalah yang timbul ketika kita mencoba untuk merencanakan suatu langkah ke depan tetapi ada agen-agen lain berencana melawan kita.
atau
Algoritma pencarian yang digunakan dalam permainan di mana satu pemain mencoba untuk memaksimalkan nilai mereka (menang) tetapi ditentang oleh pemain lain ( AI, Player Computer ).
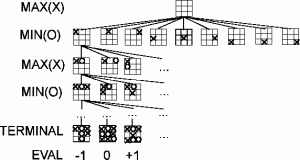
biasa digunakan untuk pencarian dalam game ( Catur, Tic Tac Toe, dll.)
Algoritma yang biasa digunakan : MiniMax, Alpha–beta pruning.
Gambar Algoritma Minimax :
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Adalah proses menemukan solusi untuk seperangkat kendala yang memaksakan kondisi yang variabel harus memenuhi. Oleh karena itu solusinya seperangkat nilai-nilai untuk variabel yang memenuhi semua kendala — yaitu titik di wilayah yang layak.
Teknik yang digunakan dalam kendala kepuasan tergantung pada jenis kendala-kendala yang sedang dipertimbangkan. Sering digunakan adalah kendala pada domain yang terbatas.
contoh : Map Coloring
2. Dalam logika matematika, kalkulus proposisional atau logika (juga disebut kalkulus sentential atau logika sentensial) adalah sistem formal di mana formula dari bahasa formal dapat ditafsirkan untuk mewakili proposisi. Sebuah sistem aturan inferensi dan aksioma memungkinkan formula tertentu untuk diturunkan. Ini rumus yang diturunkan disebut teorema dan dapat ditafsirkan sebagai proposisi benar. Seperti urutan terbuat dari formula dikenal sebagai derivasi atau bukti dan rumus terakhir dari urutan adalah teorema tersebut. Derivasi dapat ditafsirkan sebagai bukti proposisi diwakili oleh teorema.
Biasanya dalam logika proposisional Kebenaran-fungsional, formula ditafsirkan sebagai memiliki salah satu nilai kebenaran benar atau nilai kebenaran palsu. [Klarifikasi diperlukan] logika proposisional Kebenaran-fungsional dan sistem isomorfik untuk itu, dianggap logika zeroth-order.
Contoh :
Simple axiom system
Let  , where
, where 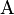 ,
, 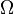 ,
, 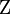 ,
,  are defined as follows:
are defined as follows:
- The alpha set
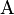 , is a finite set of symbols that is large enough to supply the needs of a given discussion, for example:
, is a finite set of symbols that is large enough to supply the needs of a given discussion, for example:
-
-
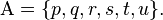
- Of the three connectives for conjunction, disjunction, and implication (
 ,
, 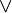 , and
, and 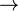 ), one can be taken as primitive and the other two can be defined in terms of it and negation (
), one can be taken as primitive and the other two can be defined in terms of it and negation ( ).[8] Indeed, all of the logical connectives can be defined in terms of a sole sufficient operator. The biconditional (
).[8] Indeed, all of the logical connectives can be defined in terms of a sole sufficient operator. The biconditional (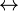 ) can of course be defined in terms of conjunction and implication, with
) can of course be defined in terms of conjunction and implication, with  defined as
defined as  .
.
- Adopting negation and implication as the two primitive operations of a propositional calculus is tantamount to having the omega set
 partition as follows:
partition as follows:
-
-

-
-

-
-
-
-
-
-
- The rule of inference is modus ponens (i.e., from
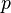 and
and  , infer
, infer  ). Then
). Then  is defined as
is defined as 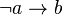 , and
, and 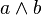 is defined as
is defined as  .
.
3.
Algoritma A*
// Astar.cpp
// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*
// Compiler: Dev-C++ 4.9.9.2
// FB - 201012256
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int n=60; // horizontal size of the map
const int m=60; // vertical size size of the map
static int map[n][m];
static int closed_nodes_map[n][m]; // map of closed (tried-out) nodes
static int open_nodes_map[n][m]; // map of open (not-yet-tried) nodes
static int dir_map[n][m]; // map of directions
const int dir=8; // number of possible directions to go at any position
// if dir==4
//static int dx[dir]={1, 0, -1, 0};
//static int dy[dir]={0, 1, 0, -1};
// if dir==8
static int dx[dir]={1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1};
static int dy[dir]={0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
class node
{
// current position
int xPos;
int yPos;
// total distance already travelled to reach the node
int level;
// priority=level+remaining distance estimate
int priority; // smaller: higher priority
public:
node(int xp, int yp, int d, int p)
{xPos=xp; yPos=yp; level=d; priority=p;}
int getxPos() const {return xPos;}
int getyPos() const {return yPos;}
int getLevel() const {return level;}
int getPriority() const {return priority;}
void updatePriority(const int & xDest, const int & yDest)
{
priority=level+estimate(xDest, yDest)*10; //A*
}
// give better priority to going strait instead of diagonally
void nextLevel(const int & i) // i: direction
{
level+=(dir==8?(i%2==0?10:14):10);
}
// Estimation function for the remaining distance to the goal.
const int & estimate(const int & xDest, const int & yDest) const
{
static int xd, yd, d;
xd=xDest-xPos;
yd=yDest-yPos;
// Euclidian Distance
d=static_cast<int>(sqrt(xd*xd+yd*yd));
// Manhattan distance
//d=abs(xd)+abs(yd);
// Chebyshev distance
//d=max(abs(xd), abs(yd));
return(d);
}
};
// Determine priority (in the priority queue)
bool operator<(const node & a, const node & b)
{
return a.getPriority() > b.getPriority();
}
// A-star algorithm.
// The route returned is a string of direction digits.
string pathFind( const int & xStart, const int & yStart,
const int & xFinish, const int & yFinish )
{
static priority_queue<node> pq[2]; // list of open (not-yet-tried) nodes
static int pqi; // pq index
static node* n0;
static node* m0;
static int i, j, x, y, xdx, ydy;
static char c;
pqi=0;
// reset the node maps
for(y=0;y<m;y++)
{
for(x=0;x<n;x++)
{
closed_nodes_map[x][y]=0;
open_nodes_map[x][y]=0;
}
}
// create the start node and push into list of open nodes
n0=new node(xStart, yStart, 0, 0);
n0->updatePriority(xFinish, yFinish);
pq[pqi].push(*n0);
open_nodes_map[x][y]=n0->getPriority(); // mark it on the open nodes map
// A* search
while(!pq[pqi].empty())
{
// get the current node w/ the highest priority
// from the list of open nodes
n0=new node( pq[pqi].top().getxPos(), pq[pqi].top().getyPos(),
pq[pqi].top().getLevel(), pq[pqi].top().getPriority());
x=n0->getxPos(); y=n0->getyPos();
pq[pqi].pop(); // remove the node from the open list
open_nodes_map[x][y]=0;
// mark it on the closed nodes map
closed_nodes_map[x][y]=1;
// quit searching when the goal state is reached
//if((*n0).estimate(xFinish, yFinish) == 0)
if(x==xFinish && y==yFinish)
{
// generate the path from finish to start
// by following the directions
string path="";
while(!(x==xStart && y==yStart))
{
j=dir_map[x][y];
c='0'+(j+dir/2)%dir;
path=c+path;
x+=dx[j];
y+=dy[j];
}
// garbage collection
delete n0;
// empty the leftover nodes
while(!pq[pqi].empty()) pq[pqi].pop();
return path;
}
// generate moves (child nodes) in all possible directions
for(i=0;i<dir;i++)
{
xdx=x+dx[i]; ydy=y+dy[i];
if(!(xdx<0 || xdx>n-1 || ydy<0 || ydy>m-1 || map[xdx][ydy]==1
|| closed_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]==1))
{
// generate a child node
m0=new node( xdx, ydy, n0->getLevel(),
n0->getPriority());
m0->nextLevel(i);
m0->updatePriority(xFinish, yFinish);
// if it is not in the open list then add into that
if(open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]==0)
{
open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]=m0->getPriority();
pq[pqi].push(*m0);
// mark its parent node direction
dir_map[xdx][ydy]=(i+dir/2)%dir;
}
else if(open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]>m0->getPriority())
{
// update the priority info
open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]=m0->getPriority();
// update the parent direction info
dir_map[xdx][ydy]=(i+dir/2)%dir;
// replace the node
// by emptying one pq to the other one
// except the node to be replaced will be ignored
// and the new node will be pushed in instead
while(!(pq[pqi].top().getxPos()==xdx &&
pq[pqi].top().getyPos()==ydy))
{
pq[1-pqi].push(pq[pqi].top());
pq[pqi].pop();
}
pq[pqi].pop(); // remove the wanted node
// empty the larger size pq to the smaller one
if(pq[pqi].size()>pq[1-pqi].size()) pqi=1-pqi;
while(!pq[pqi].empty())
{
pq[1-pqi].push(pq[pqi].top());
pq[pqi].pop();
}
pqi=1-pqi;
pq[pqi].push(*m0); // add the better node instead
}
else delete m0; // garbage collection
}
}
delete n0; // garbage collection
}
return ""; // no route found
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
// create empty map
for(int y=0;y<m;y++)
{
for(int x=0;x<n;x++) map[x][y]=0;
}
// fillout the map matrix with a '+' pattern
for(int x=n/8;x<n*7/8;x++)
{
map[x][m/2]=1;
}
for(int y=m/8;y<m*7/8;y++)
{
map[n/2][y]=1;
}
// randomly select start and finish locations
int xA, yA, xB, yB;
switch(rand()%8)
{
case 0: xA=0;yA=0;xB=n-1;yB=m-1; break;
case 1: xA=0;yA=m-1;xB=n-1;yB=0; break;
case 2: xA=n/2-1;yA=m/2-1;xB=n/2+1;yB=m/2+1; break;
case 3: xA=n/2-1;yA=m/2+1;xB=n/2+1;yB=m/2-1; break;
case 4: xA=n/2-1;yA=0;xB=n/2+1;yB=m-1; break;
case 5: xA=n/2+1;yA=m-1;xB=n/2-1;yB=0; break;
case 6: xA=0;yA=m/2-1;xB=n-1;yB=m/2+1; break;
case 7: xA=n-1;yA=m/2+1;xB=0;yB=m/2-1; break;
}
cout<<"Map Size (X,Y): "<<n<<","<<m<<endl;
cout<<"Start: "<<xA<<","<<yA<<endl;
cout<<"Finish: "<<xB<<","<<yB<<endl;
// get the route
clock_t start = clock();
string route=pathFind(xA, yA, xB, yB);
if(route=="") cout<<"An empty route generated!"<<endl;
clock_t end = clock();
double time_elapsed = double(end - start);
cout<<"Time to calculate the route (ms): "<<time_elapsed<<endl;
cout<<"Route:"<<endl;
cout<<route<<endl<<endl;
// follow the route on the map and display it
if(route.length()>0)
{
int j; char c;
int x=xA;
int y=yA;
map[x][y]=2;
for(int i=0;i<route.length();i++)
{
c =route.at(i);
j=atoi(&c);
x=x+dx[j];
y=y+dy[j];
map[x][y]=3;
}
map[x][y]=4;
// display the map with the route
for(int y=0;y<m;y++)
{
for(int x=0;x<n;x++)
if(map[x][y]==0)
cout<<".";
else if(map[x][y]==1)
cout<<"O"; //obstacle
else if(map[x][y]==2)
cout<<"S"; //start
else if(map[x][y]==3)
cout<<"R"; //route
else if(map[x][y]==4)
cout<<"F"; //finish
cout<<endl;
}
}
getchar(); // wait for a (Enter) keypress
return(0);
}















 , where
, where 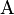 ,
, 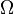 ,
, 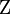 ,
,  are defined as follows:
are defined as follows: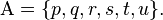
 ,
, 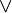 , and
, and 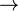 ), one can be taken as primitive and the other two can be defined in terms of it and negation (
), one can be taken as primitive and the other two can be defined in terms of it and negation ( ).
).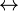 ) can of course be defined in terms of conjunction and implication, with
) can of course be defined in terms of conjunction and implication, with  defined as
defined as  .
. partition as follows:
partition as follows:

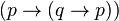


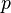 and
and  , infer
, infer  ). Then
). Then  is defined as
is defined as 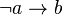 , and
, and 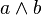 is defined as
is defined as 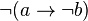 .
.